Difference between revisions of "Shared:Group 4"
(→Video Sample of Prototype) |
|||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
==Video Sample of Prototype== | ==Video Sample of Prototype== | ||
| − | < | + | |
| + | <youtube width="560">53mm6VAaA-c</youtube> | ||
=='''Code Sample'''== | =='''Code Sample'''== | ||
Revision as of 00:50, 21 April 2017
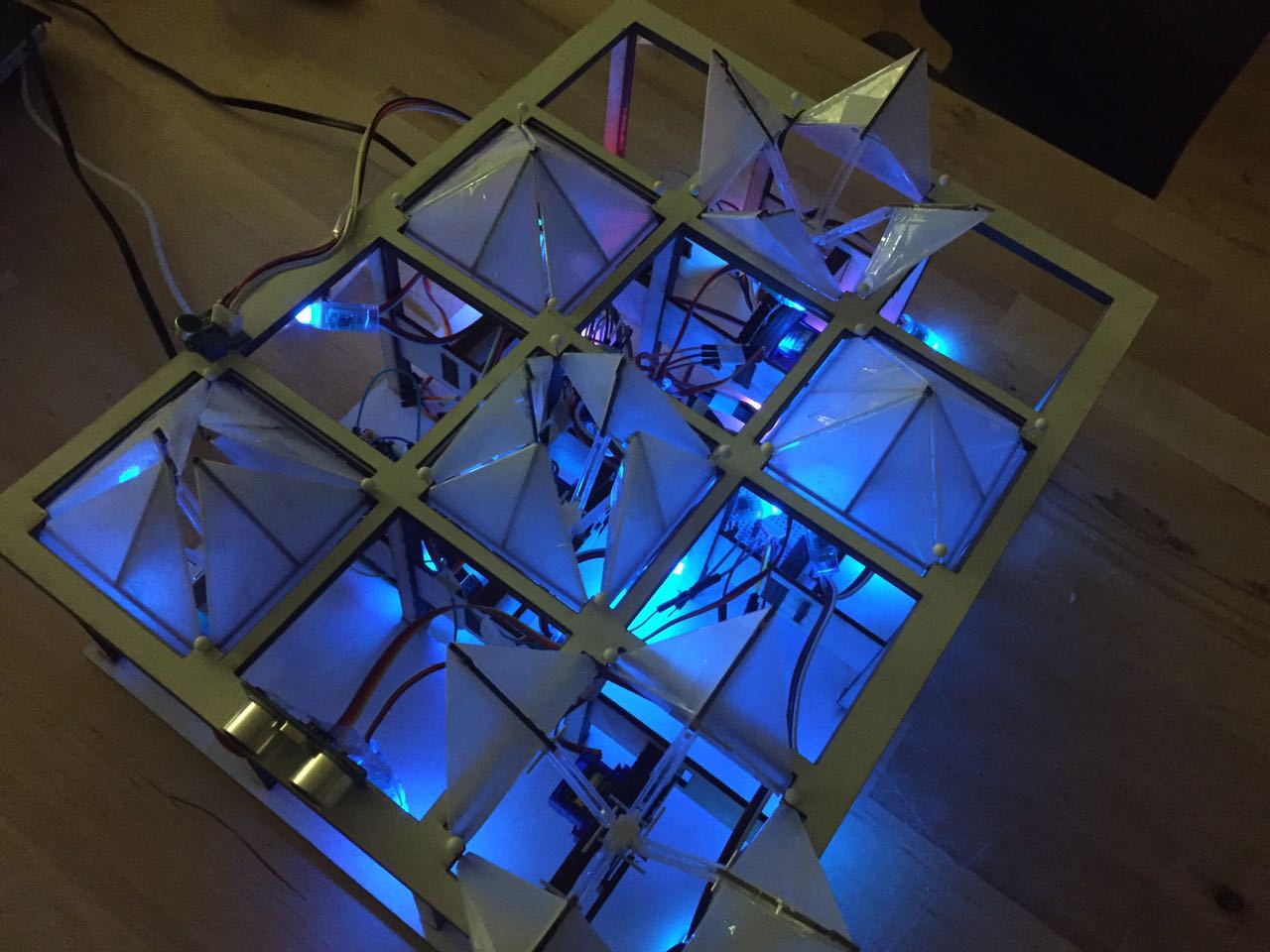
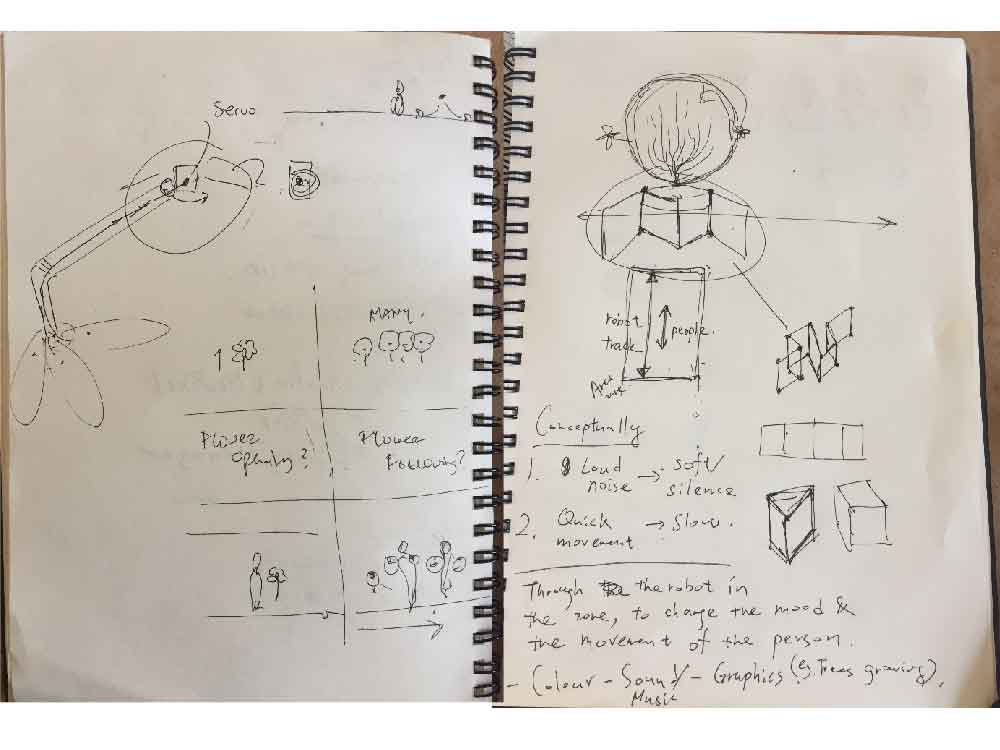
Flower_blooming_process_in_reaction_to_people_interaction , by Danny, Boyuan
Video Sample of Prototype
Code Sample
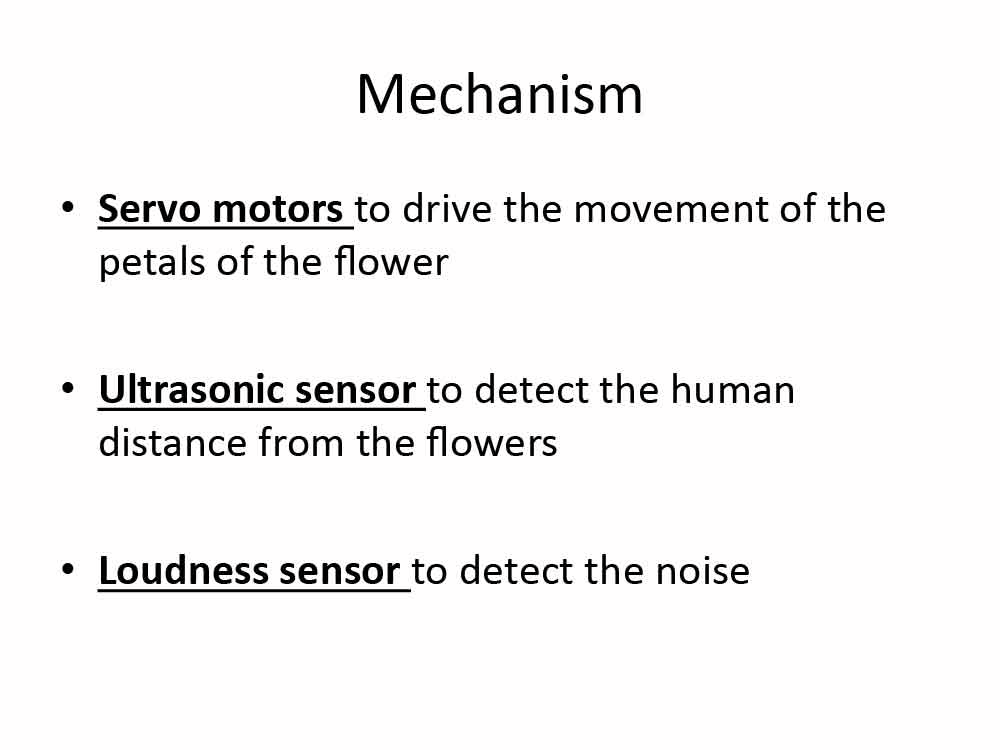
The code works by mapping the ultrasonic distance sensor data into the servo motor. So that the shorter the distance the sensor detected, the larger angle the servo motor turns and the flower will open. When the distance recorded is long, the servo motor will turn back to smaller angle and the flower will close.
- include <Servo.h>
Servo myservo1; Servo myservo2; Servo myservo3; Servo myservo4; Servo myservo5; Servo myservo6; Servo myservo7; // twelve servo objects can be created on most boards
- define trigPin 10
- define echoPin 11
- define PREVIOUS_VALS 25
int potpin = 0; // analog pin used to connect the potentiometer float val; // variable to read the value from the analog pin
float historyVals[PREVIOUS_VALS];
- define timeScale 6
float averageVals[7 * timeScale];
void setup() {
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT);
Serial.begin (9600);
myservo1.attach(3);
myservo2.attach(4);
myservo3.attach(5);
myservo4.attach(6);
myservo5.attach(7);
myservo6.attach(8);
myservo7.attach(9);
float initialVal = 90;
for (int i = 0; i < PREVIOUS_VALS; i++) {
historyVals[i] = initialVal;
}
}
void loop() {
float duration, distance;
distance = 9999999;
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH); delayMicroseconds(10); digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
duration = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH); distance = (duration / 2) * 0.0344;
Serial.println(distance); delay(30);
if (distance > 100 || duration > 500000) {
distance = 50;
}
val = mapfloat(distance, 1, 50, 50, 180); // scale it to use it with the servo (value between 0 and 180) //Serial.println(val); //Serial.println(val, 10);
addValToHistory(val);
float currentAverage = averageVal();
addAverageToHistory(currentAverage);
writeServos();
delay(10);
}
float mapfloat(float x, float in_min, float in_max, float out_min, float out_max) {
return (x - in_min) * (out_max - out_min) / (in_max - in_min) + out_min;
}
float averageVal() {
float total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < PREVIOUS_VALS; i++) {
total = total + historyVals[i];
}
float average = total / PREVIOUS_VALS;
return average;
}
void addValToHistory(float v) {
for (int i = 0; i < PREVIOUS_VALS - 1; i++) {
historyVals[i] = historyVals[i + 1];
}
historyVals[PREVIOUS_VALS - 1] = v;
}
void addAverageToHistory(float av) {
for (int i = 0; i < 7 * timeScale - 1; i++) {
averageVals[i] = averageVals[i + 1];
}
averageVals[7 * timeScale - 1] = av;
}
void writeServos() {
int i = 7 * timeScale - 1; myservo1.write(averageVals[i]); i = i - timeScale; myservo2.write(averageVals[i]); i = i - timeScale; myservo3.write(averageVals[i]); i = i - timeScale; myservo4.write(averageVals[i]); i = i - timeScale; myservo5.write(averageVals[i]); i = i - timeScale; myservo6.write(averageVals[i]); i = i - timeScale; myservo7.write(averageVals[i]);
}